The world's first living, self-healing robots 1:25
(CNN) -
American scientists who created the first living robots claim that these life forms, known as xenobots, can already reproduce, and in a way that has not been seen in plants and animals.
Formed from the stem cells of the African clawed frog (Xenopus laevis) from which it takes its name, xenobots are less than a millimeter wide.
The tiny spots were first unveiled in 2020 after experiments showed they could move, work in groups, and heal themselves.
Intact brain cells from almost 2,000 years ago found
Now the scientists who developed them at the University of Vermont, Tufts University, and the Wyss Institute for Biology-Inspired Engineering at Harvard University say they have discovered an entirely new form of biological reproduction not seen in any known animal or plant. by science.
"I was in awe," said Michael Levin, professor of biology and director of the Allen Discovery Center at Tufts University, who co-authored the new research.
"Frogs have a way of reproducing that they normally use, but when (...) they are freed (the cells) from the rest of the embryo and given the opportunity to discover how to be in a new environment, they not only discover a new way to move, but also apparently discover a new way to reproduce. "
https://cnnespanol.cnn.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/WEBTAGXenobotsAIcontrolledselfreplication.mp4
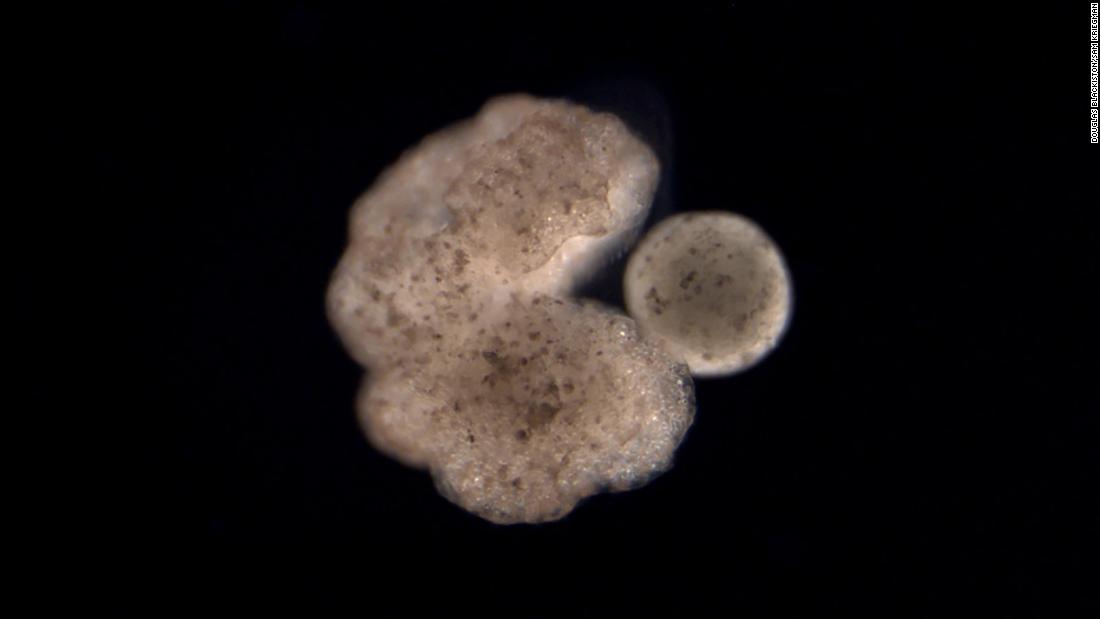
The C-shaped parent xenobots collect and compress the loose stem cells into clumps that can mature into young.
advertising
Robot or organism?
Stem cells are unspecialized cells that have the ability to turn into different types of cells.
To make the xenobots, the researchers extracted living stem cells from frog embryos and allowed them to incubate.
There was no gene manipulation.
"Most people think robots are made of metals and ceramics, but it's not so much about what a robot is made of as what it does, which is acting for itself on behalf of the people," Josh said. Bongard, a professor of computer science and robotics expert at the University of Vermont and lead author of the study.
An Argentinean is the second HIV patient who could have been "cured" of the infection without stem cell treatment, in an extremely rare case
"In that sense it is a robot, but it is also clearly an organism made from non-genetically modified frog cells."
Bongard said they found that xenobots, which were initially sphere-shaped and made of about 3,000 cells, could replicate.
But this happened rarely and only in specific circumstances.
The xenobots used "kinetic replication," a process that is known to occur at the molecular level but has never been observed at the scale of cells or whole organisms, Bongard said.
With the help of artificial intelligence, the researchers tested billions of body shapes to make the xenobots more effective at this type of replication.
The supercomputer came up with a C-shape that resembled "Pac-Man," the video game from the 1980s. They discovered that the xenobot was capable of finding tiny stem cells in a Petri dish, gathering hundreds of them inside its mouth, and A few days later, the cell pool turned into new xenobots.
https://cnnespanol.cnn.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/WEBTAGXenobotsparentrotatingalargeballofstemcells.mp4
The parent spins a large ball of stem cells that is maturing into a new xenobot.
"The AI didn't program these machines the way we usually think of writing code. It modeled and sculpted until it came up with this 'Pac-Man' shape," explains Bongard.
"The form is, in essence, the program. The form influences the behavior of the xenobots to amplify this incredibly amazing process."
Xenobots are a very early technology, think of a 1940's computer, and they don't have any practical applications yet.
However, according to the researchers, this combination of molecular biology and artificial intelligence could be used in a myriad of tasks in the body and the environment.
This could include things like collecting microplastics from the oceans, inspection of root systems, and regenerative medicine.
Although the prospect of self-replicating biotechnology might raise concern, the researchers claimed that living machines are fully contained in a laboratory and are easily extinguished, as they are biodegradable and regulated by ethicists.
Electric robots are mapping the seafloor, Earth's last frontier
The research was partially funded by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency, a federal agency that oversees the development of technology for military use.
"There are many things that are possible if we take advantage of this type of plasticity and ability of cells to solve problems," said Bongard.
The research was published this Monday in the scientific journal PNAS.
- Jessie Yeung contributed to this report from Hong Kong.
Stem cells Robot


/cloudfront-eu-central-1.images.arcpublishing.com/prisa/QZBKEHFL6RHI5FSPQNNBZGIIUA.jpg)