This phenomenon can interfere with vision. Here's how to fix it
Feel a fleshy "membrane" on the eye that causes discomfort and impair vision? Don't worry, it's probably not a cancerous tumor, but a removable patrigium in a relatively simple surgery, accompanied by local treatment to prevent recurrence
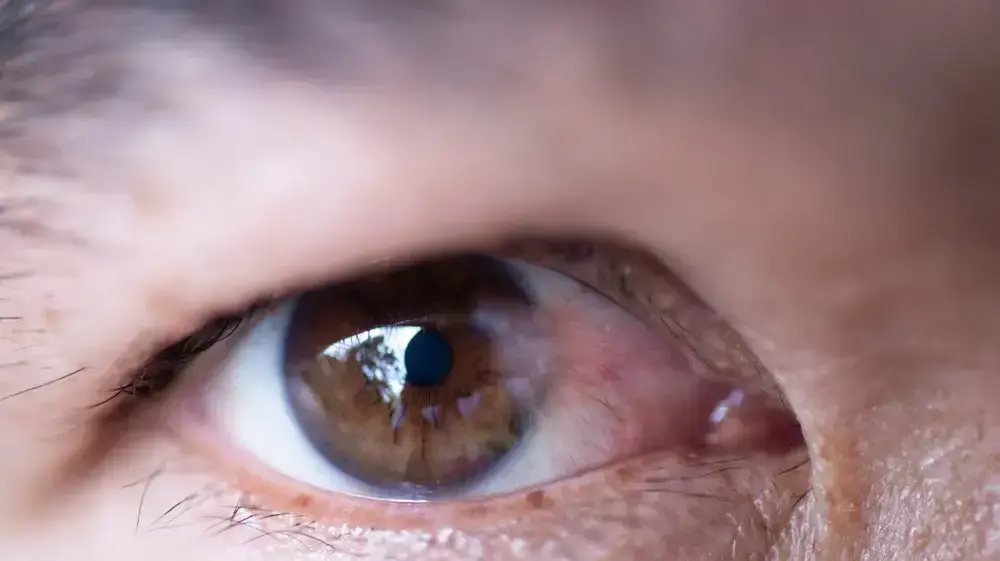
The reason: degenerative change due to sun exposure. Patriarchate (Photo: ShutterStock)
Patriarchate (Photo: ShutterStock)
Pterygium (and in Hebrew: Snail) is a sort of fleshy membrane that grows gradually from the conjunctiva - and from there across the cornea - and can cause visual, discomfort and aesthetic disturbance. However, patrigium is not a cancerous tumor and can be removed in a relatively simple analysis.
More in Walla! NEWS More in Walla! NEWSEye disease that also affects children - and the way to treat it
To the full articlePatrigium is a pink, fleshy tissue that grows from the conjunctival direction of the eye (the transparent layer that covers the whiteness of the eye and the inner side of the eyelids) as a result of a degenerative change that occurs due to exposure to the sun's radiation. Usually, it appears first on the side that is closer to the nose and spreads away toward the pupil. The patrigium develops gradually and at different rates in different people and may appear in one or both eyes, and in the same eye from both the inner and outer sides ("bilateral patrigium"). In some cases, its development stops early (before approaching sleep), but if it continues to grow, it can interfere with vision.
What Are The Causes Of Patriotium?
To date, it is not yet known what causes the development of patri- gium, but it is known that there is long-term exposure to the sun, dry climate, sand and dust. It is also known that there is a certain (genetic) family connection. Therefore, the phenomenon is more common among people with a family history of patrigium. As a precursor to the development of the patrigium, in many cases one finds a pinguecula or spice, a small protrusion, sometimes yellowish on the inner or outer side of the eye.
What are the symptoms?
Early stages include symptoms of persistent redness, inflammation, foreign body sensation in the eye, eye dryness, itching, and sometimes the feeling that something "hides the field of vision". As the patrigium grows and spreads toward the center of the eye, it may block the axis of vision and / or distort the cornea. As a result, it can cause a high cylinder and decreased vision. Beyond the clinical symptoms, patrigium is also a prominent aesthetic problem, which disturbs many patients.
What is the recommended treatment for Patrigium?
As long as the patrigium is small and does not interfere with vision, it can be treated with a conservative approach, through tears replacements, preparations that cause constriction of the blood vessels in the conjunctiva and eye bleaching, and the wearing of sunglasses to reduce exposure to UV rays. In cases where the patrigium is large, disturbed with vision, or spreads toward the center of vision - surgery is required to remove it. Even if the patrigium disturbs the patient aesthetically, surgery can be considered.
How is Patrigium treated by surgery?
Patrigium removal surgery is a relatively simple operation, lasting about 30-15 minutes and performed under local anesthesia. During surgery, the patrigium tissue is separated and removed from the conjunctival and corneal tissues. Previously, the surgery ended with the removal of the patrigium. In those days, the rate of post-operative patrigium was about 50-70 percent. Therefore, today, after the removal phase, another action is taken to prevent the recurrence.
There are currently three surgical approaches to prevent patriarchal recurrence. All methods are similar in their chances of success and reduce the return rate to about 3-5 percent.
When to analyze?
In the past, due to the high recurrence rates, surgery was only performed when the patrigium was very advanced. Nowadays prefer not to wait for a large patricium because the removal also leaves scars in the cornea and sometimes the cosmetic result is less beautiful when the initial patrigium is already large. Therefore, surgeons when the growth and activity of the patrigium is documented, when it is prominent and elevated, and creates a sense of discomfort in the eye, when the patrigium adversely affects the vision, whether it causes distortion and a cylinder or concealment in the visual field and of course even if there is aesthetic disorder.
"Chemical" action
This graft is not used, but rather placed on a small sponge containing a very low concentration of chemotherapeutic drug called mitomycin C, for about two minutes, after which the area is rinsed well. The material helps to eliminate the problematic cells that form the patrigium.
"Free" conjunctival implant
In this approach, fill the empty space created with a conjunctival conjunctiva, taken from the conjunctival "reserve" in the upper part of the eye (under the eyelid). The "borrowed" conjunctival tissue is implanted with special adaptation in the limbo region - the conjunctival region of the conjunctiva with the cornea, where the corneal stem cells are. Transplantation in this area allows the stem cells of the cornea to be transferred from the top to the nasal side of the nose, thus creating a condition where the stem cells create a kind of "arrest" that prevents the patrigium from growing again.
Implant a conjunctiva with a rack
This approach also fills in the blanks with the existing conjunctival reserve, but in contrast to the previous approach, this approach does not harvest and implant the conjunctiva in the designated area, but "pulls" the conjunctival reserve down to cover the missing area. Sometimes, in cases where the patrigium recurrence occurs, the two methods are combined - an implant with mitomycin C. This is to reduce as much as possible the additional recurrence.
Seams or biological glue?
When using the free implant approach, the implant can be attached using sutures or with biological adhesive. In general, biological glue can be said to have a certain advantage over sutures, even in terms of recovery period (sutures create a foreign body feel to the eye). Beyond that, biological adhesive has another small advantage, in terms of lowering the risk of recurrence. However, the biological adhesive is very expensive, and therefore also lowers the costs of surgery. Thus, the choice is usually made on cost-convenience considerations.
What is recommended to do in case there is both a patricium and a cataract?
Generally, in cases where the patient has both a patrigium and a cataract, it is preferable to first remove the patrigium, and after several months to perform a cataract removal operation. This is because the patrigium often forms a cylinder. Once the patrigium is removed, the cornea changes again and receives a new cylinder (usually a smaller cylinder). Therefore, it is best to wait several months to perform the cataract surgery again and know what the final cylinder is.
In cases where the patient has both a patrigium and a cataract, both can sometimes be removed together, but the preference is to treat the patrigium first. After a few months' recovery, biometric measurements are repeated, and cataract surgery can also be corrected if astigmatism is created, if it has been created by the patrigium.
What does the Patrigium Removal Surgery entail?
The surgery is an external eye surgery and is therefore not a relatively dangerous surgery. Because of the fact that being on the outside of the eye, the healing is less pleasant and can involve pain and discomfort. In the first two days and then for less than a fortnight or so. Most often, after about six weeks of surgery, the eye returns to looking white as usual.
Do any complications and side effects have to be analyzed?
As mentioned, surgery is not considered relatively dangerous. Blood thinners should be stopped (if the patient is taking blood thinners). One of the possible complications on the first day after surgery used in the implant is the implant's loss or loss, as a result of eye rubbing, for example. In this case, surgery can be restored without implant, and if there is recurrence of the patrigium, it can be re-analyzed. There may also be a problem with the implant absorption up to its dissolution and disappearance.
Another complication is related to the implant swelling in the early stages of its absorption, creating a nearby area that does not get enough shielding from the tears until dehydration and creating a dent in the eye wall. Usually under topical ointment and steroid treatment, there is complete recovery.
There may be an exaggerated and unexpected stitching reaction until a red protrusion develops in the area. Usually again under the treatment of lubricants and steroidal drops and ointments, the problem is fully resolved.
Side effects that may be post-operative: eye dryness and unpleasant sensations, redness and blood flow. These effects are treated with ointments and drops that add moisture to the eye. As mentioned, the phenomena go away a few weeks later.
Importantly, the surgery is not intended to improve vision, although there is sometimes an improvement in postoperative vision. The surgery is designed to stop the progression of the patrigium, thereby stopping the deterioration of vision.
Dr. Adi Michaeli is an Ophthalmologist, a specialist in cataract surgery and corneal surgery at the Intel Medical Center
Helped to prepare the article: Yaarit Treblassi, a zap doctors reporter