Microplastics dispersed in the oceans have extremely negative effects on the life of small marine organisms, endangering the life cycle of all species and their regulatory function of the global ecosystem.
It is the result of the research "Plastics, (bio) polymers and their apparent biogeochemical cycle: an infrared spectroscopy study on foraminifera", published by the journal "Enviromental Pollution" and signed by Giovanni Battista De Giudici, Carla Buosi and Daniela Medas, specialists of the Department of Chemical and Geological Sciences of the University of Cagliari with some researchers from other universities.
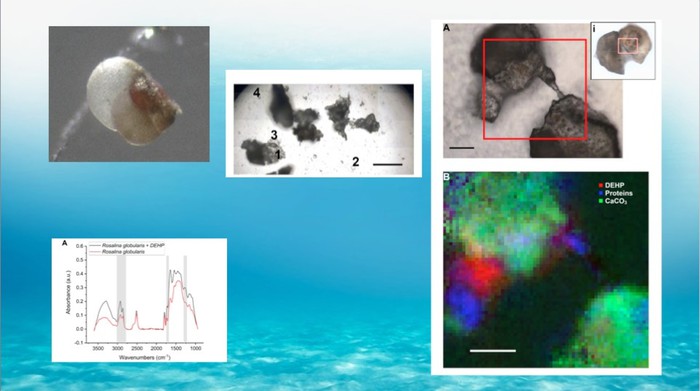
The activity focused on the effects of industrially produced microplastics (which contain the plasticizer DEHP) on the shells and cytoplasm of foraminifera, single-celled marine organisms, present everywhere in the sea and which represent one of the entrances to the food chain.
A positive effect of the presence in the sea of many species of foraminifera is determined by their shell of calcium carbonate which helps in reabsorbing atmospheric CO2.
Research results show that microplastics are present in the shell and cell of the analyzed foraminifera.
By studying the compositional spectrum of cells, it was shown for the first time that the presence of plastics induces cellular stress in these microorganisms.
Furthermore, DEHP plasticizer is incorporated into the cell and also into the shell.
"These observations lead us to think that chemical pollution combined with the acidification of water can lead to the disappearance of foraminifera by 2100 - explains De Giudici - An eventuality to be avoided, because foraminifera are a fundamental component of the ecosystem and their biodiversity and abundance are essential elements for environmental resilience with respect to Global Changes ".


/cloudfront-eu-central-1.images.arcpublishing.com/prisa/2RQK76CJRZCS5KCBA56WRJ5CEU.jpg)










/cloudfront-eu-central-1.images.arcpublishing.com/prisa/IGZ7GOCXZ5GUPAQ2HWGK6Z76BU.jpg)