Antigen testing has become the main way to detect coronavirus infection in the sixth wave.
With a saturated health system, the authorities recommend rapid pharmacy tests so that citizens isolate themselves if they test positive and, some communities are even processing withdrawals by this same method.
The reliability of antigen tests is not as good as PCR, but they have several advantages: they are faster, cheaper, can be done at home and, at least until the arrival of omicron, they have been shown to be sufficiently sensitive when the person it has a higher viral load and is therefore more contagious.
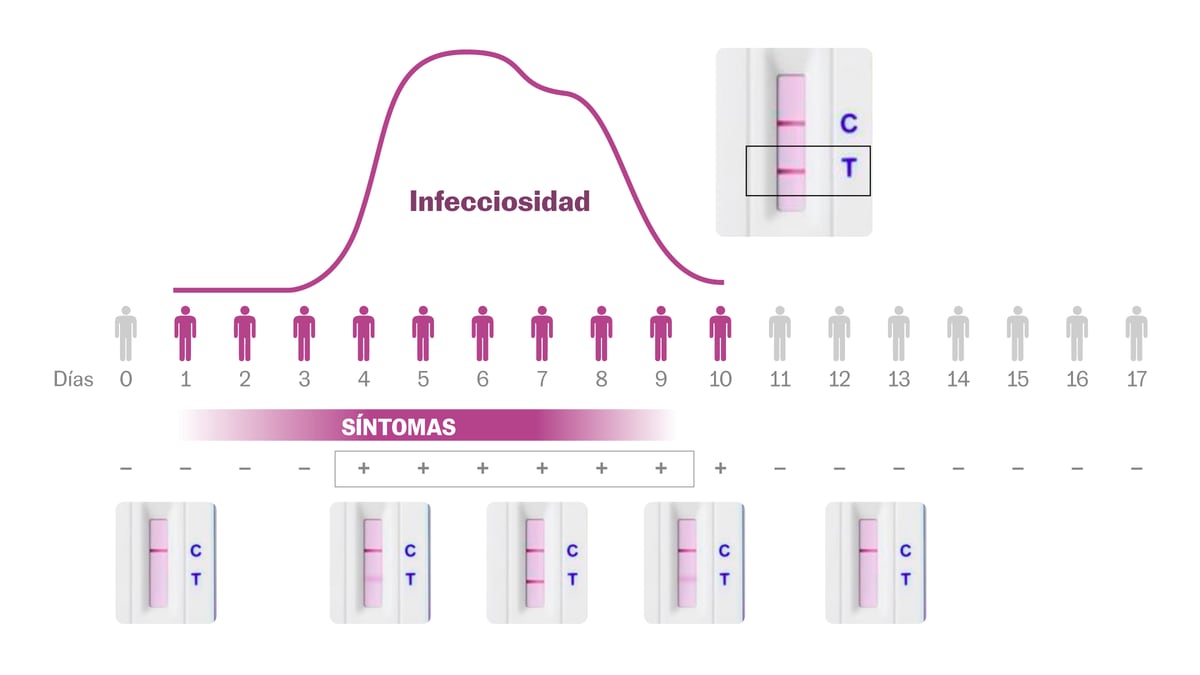
The tests can mark two lines.
The first is the control and the second, where the letter T appears, indicates that it has detected a viral load in the sample.
Whatever the intensity of this second line, if it appears it means that the result is positive.
Just because a second line does not appear does not mean that there is no infection.
A positive is fairly reliable in detecting a contagion, but a negative can mean that there is still not enough viral load and the virus is incubating.
In addition, a novelty with the omicron variant is that the symptoms can appear before the positive one, when the viral load is low.
After an outbreak in Norway, it was discovered that most of those infected began to have signs of the disease (cough, sore throat, fever ...) between three and four days after contact.
Epidemiologist Michael Mina has underlined this: "The relationship between the onset of symptoms and the peak of viral load has changed."
This may be due to the characteristics of the variant or the fact that it causes more reinfections and that our body reacts differently to them.
Given the suspicion of contagion, it is advisable to do more than one test, since it is possible that in the first days, the test still does not detect the virus and it will do so as the infection progresses.
If you have symptoms, even if it is negative, extreme precautions should be taken.
One could be infected and perhaps infect.
This is what a recently published small preliminary study suggests, "most omicron cases were infective for several days before being detectable by a rapid antigen test."
That is why it is advisable to be cautious, as Mina suggests: “If you are symptomatic and negative […] you must be very, very careful.
Even isolate yourself, if possible, and take a test the next morning or that night.
The more viral load the test detects, the second line will appear darker.
The normal thing is that in the first and last days of infection it appears lighter and in the central ones darker.
The protocol in Spain indicates that a seven-day isolation must be started from the positive, regardless of whether it is suspected that this occurred in an earlier or later stage of infection, whether the second line is lighter or darker.
If it is a home test, the patient must notify the health authorities.
If the symptoms are mild, isolation is enough, which can end seven days after self-diagnosis, provided the patient has been symptom-free for three days.
Otherwise, the isolation must be extended to 10 days.
If symptoms persist, worsen (high fever, shortness of breath), contact a doctor.

/cloudfront-eu-central-1.images.arcpublishing.com/prisa/56U4ECEFCRDAFOPWRKT642I7WI.jpg)





