An autistic child with a teacher (Photo: ShutterStock)
A new study led by Hebrew University researcher Dr. Haitam Amal and his research group, from the School of Pharmacy at the Faculty of Medicine, found that there is a significant link between levels of nitric oxide (NO) in the brain and autism.
The study, published today in the prestigious journal Advanced Science, proved that with the increase in nitric oxide in the brain, so do the indicators of autism. Conversely, in cases where, proactively and controlled, the levels of oxide in the brains of laboratory animals with a genetic mutation that causes autism in humans were lowered, the indicators and autistic behavior decreased respectively. Dr. Amal is the first in the world to crack this new mechanism in autism.
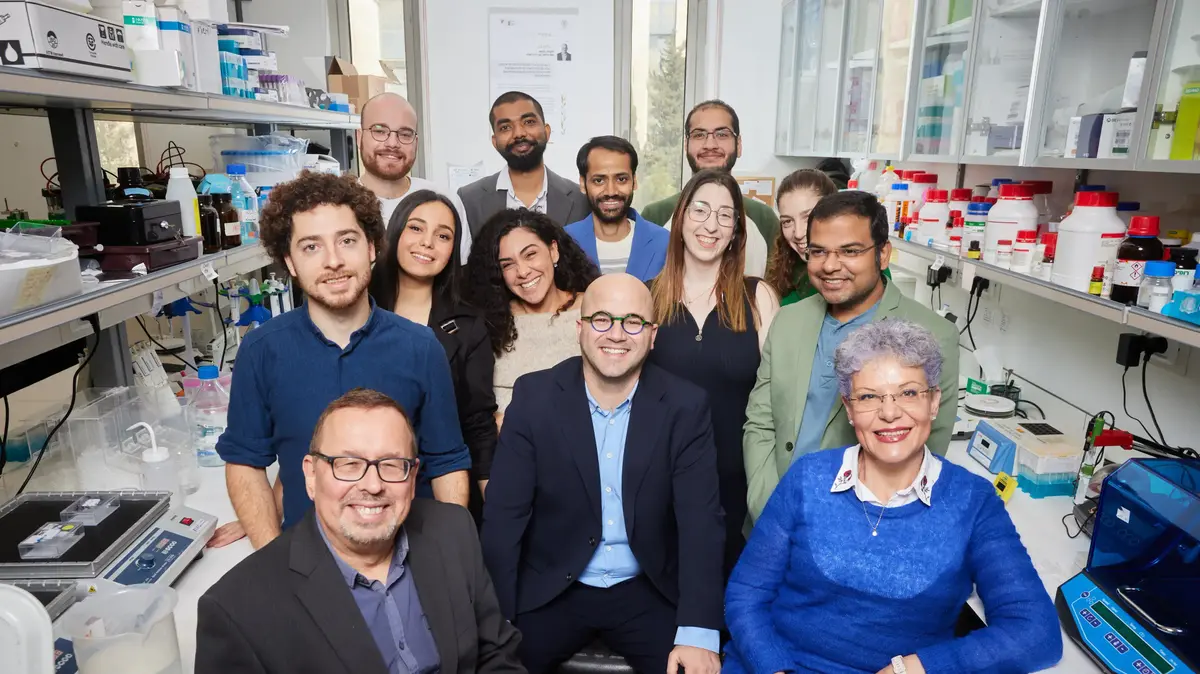
Dr. Amal together with his laboratory staff Dr. Manish Tripathi, Shank Uja, Miriam Kartawi and Wagyha Hamudi (Photo: Igor Berfabrov)
Today, millions of people around the world struggle with autism spectrum disorders. In Israel alone, more than 30,18 children up to the age of 1 have been diagnosed with autism. In the United States, 44 in 21 people under the age of <> are on the autism spectrum, according to data from the US Centers for Disease Control, making it the most common developmental disorder in the United States. In the current study, in an innovative and groundbreaking way, researchers showed that there is a close connection between the two elements - nitric oxide in the brain and autism. The results are based on tests in laboratory animals and in various low-functioning autistic models. Among these, various parameters were examined: problems with social communication, repetition and behavioral repetitiveness, lack of interest in new objects, anxiety, etc. In addition, human stem cells and clinical blood samples of children with low-functioning autism were examined.
More in Walla!
The leading HMO presents: The services that will make your life easier
In collaboration with Clalit
Hope for developing a cure for autism
Dr. Amal and his lab staff Dr. Manish Tripathi, Shank Uja, Miriam Kartawi and Wagyha Hamudi found that when they actively worked to lower nitric oxide levels in the brain, autistic behavior decreased correspondingly. "Our study has shown exceptionally well that inhibition of nitric oxide production in neurons in the brain in autistic models in the laboratory causes a decrease in autistic markers. The laboratory animals we examined became more "social", less repetitive behavior was observed, and they were interested in new objects, we also saw that they were less anxious. In addition, the inhibition of nitric oxide levels led to a significant improvement in neuronal indicators," Dr. Amal explained.
"This is the first time that a laboratory has been able to discover and prove a real link between an increase in nitric oxide concentration in the brain and autistic behavior, which constitutes a significant breakthrough in autism research worldwide. The discovery could have implications for the association of nitric oxide with other neurological diseases, such as Alzheimer's, or psychiatric diseases such as schizophrenia and manic-depression," concluded Dr. Amal, adding: "I hope that the new discovery and understanding of this mechanism will lead to the real possibility of developing a cure for autism. In my view, such a drug will help millions of children and adults, around the world, who suffer from the disorder."
- health
- news
Tags
- autism