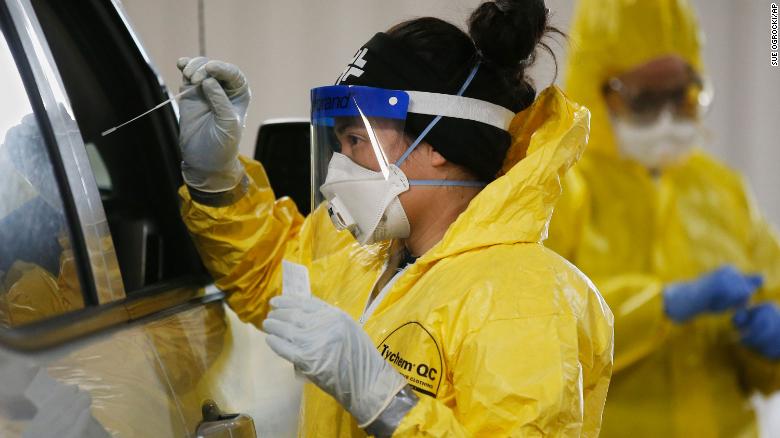
Covid-19 rapid test prices rise 0:52
(CNN Spanish) -
As infections of the omicron variant of the coronavirus continue to increase in the world, at a rate that we have not seen before, the demand for covid-19 tests has also exploded.
In the United States, home tests are hard to come by and have risen in price, and places where these tests are performed have seen mile-long lines for weeks.
Mass testing, as well as vaccination, continue to be essential tools to slow the advance of the pandemic.
What types of covid-19 tests are there?
What is the most recommended?
Why are the results delayed?
This is what we know:
Types of covid-19 tests: PCR / antigens and antibodies
Although it seems that there are many test options to detect the virus, they all fall into two: those that detect the presence of the virus and those that detect if there was a previous infection.
Genetic material (RNA) or antigens are used to detect if the virus is active (commonly referred to as the PCR test and the antigen test).
The serology test, the antibody test, seeks to detect if the body has had an immune response to the coronavirus, and therefore was exposed to the covid-19 virus.
Not only are rapid covid-19 home tests rare, but now more expensive too
The test known as PCR is the one that uses RNA and that is mostly done by taking a sample with swabbing in the nasopharyngeal area, explains Dr. Felipe Lobelo, director of the Exercise is Medicine Global Research and Collaboration Center at Emory University in Atlanta, USA This type of test can also be done on a saliva sample.
"Both tests require that the samples be sent to a laboratory to carry out the process of detecting the virus genome by means of PCR," adds Lobelo.
advertising
Diagnostic antigen tests "can be done in the laboratory or on a machine that gives the results quickly. These generally have a high% of false negatives so sometimes they require an additional PCR test," explains Dr. Lobelo.
Regarding the antibody test, the virologist Maria Fernanda Gutiérrez, from the Javeriana University of Bogotá, explains that the serological tests "are not diagnostic, they serve as a screening to see how much contact has been had with the virus. A person who has had contact with the virus it has antibodies. It does not tell me that I am infected at this moment, it tells me that I am or have been in contact with the virus ".
PCR test for covid-19
What are they?
Polymerase chain reaction tests, known as PCR, are the most common and accurate tests to determine if someone is currently infected with the new coronavirus.
How do they work?
Each virus has a unique genetic code.
The new coronavirus PCR test works by starting with a throat swab or sputum sample from a patient, amplifying that sample on a machine, and then looking for unique coronavirus genetic material.
First, a healthcare worker takes a swab or sputum sample from the back of the patient's throat or nose, usually using a long, thin nasopharyngeal swab.
That swab is stored in a sterile tube or vial and then sent to a lab that has access to a test kit.
Covid-19 home tests are less sensitive to omicron variant, FDA says
There, trained laboratory technicians extract any genetic information from the sample.
The purified genetic material is then mixed with materials, including some derived from the coronavirus itself, which are known as reagents.
The entire solution is then placed in a toaster-sized testing machine.
If a patient's sample contains coronavirus, the genetic material of the virus will be amplified and the machine will give a positive result.
And if the sample does not have coronavirus, there will be a negative result.
Generally, the entire process can be measured in days, although the time to obtain a result is shorter if hospitals or clinics have in-house test kits.
Antigen tests
What are they?
Antigen tests are a quick and easy way to look for a specific antigen, a term for any foreign substance, such as a virus or bacteria.
Antigen tests for the flu or strep throat, for example, can be performed in a doctor's office without expensive equipment and give results in minutes.
How do they work?
Consider a home pregnancy test.
In a coronavirus antigen test, you place a body sample, such as a throat swab, on a specially treated strip, which then uses a color or marker to indicate whether the new coronavirus is present.
The antigen test works by looking for a unique part of the new coronavirus, such as a specific protein in one of the "corona" peaks.
If that specific protein is present in detectable amounts, the test is positive.
Covid-19 vaccines prevent death but not contagion 1:29
Covid-19 antibody tests
What are they?
Antibody tests, also known as serological tests, do not detect the virus itself.
Instead, they detect if someone has the antibodies in their immune system to fight the new coronavirus.
People develop antibodies when their body fights the virus.
How do they work?
Antibody tests are done on a sample of blood.
This can be from a finger stick or a vein.
Most antibody tests require a trained expert to examine that blood sample for antibodies specifically targeting the coronavirus.
Our bloodstream has a library of antibodies against various viral, bacterial and fungal infections we've had throughout our lives, said Dr. Kent Sepkowitz, CNN medical analyst who specializes in infectious diseases.
The goal of this test is to find the antibody that specifically applies to the new coronavirus that causes covid-19.
However, there are seven different coronaviruses that cause illness in humans, including several that cause mild symptoms like the common cold.
Our antibodies to each coronavirus appear similar, so deciphering between the common cold antibody and the covid-19 antibody is a real challenge scientifically, Sepkowitz said.
Specialists fear shortage of monoclonal antibodies against covid-19
What is the most reliable?
"They are all reliable," Dr. Gutiérrez explains to CNN.
Gutiérrez points out that there are many companies that perform both PCR and antigen tests, with different margins of error.
"If I start to compare what is better, if to detect the RNA and amplify it, (...) or detect antibodies, well that depends on what you want. In general, what is more sensitive for the diagnosis is to amplify the viral RNA, which it is the real-time PCR test. It is undoubtedly the most sensitive, it shows me the presence of the virus, "he explains.
Dr. Lobelo agrees in calling the PCR the most reliable.
"They require laboratory processes to amplify the RNA of the virus to be able to detect it. That is why it is more reliable but takes longer (approximately 6 hours minimum)."
Long lines at covid-19 testing centers in Argentina 1:34
And why are some COVID-19 test results taking so long?
"It is not an easy test to do," explains Dr. Gutiérrez. "You start with the sample, which is considered to be infectious. If I take a sample from a patient with the virus, then the virus is there and the person taking the sample is exposed. From then on the sample has to be handle in containment 3 biosafety laboratories to prevent the person who is working with it from being exposed and infected ".
"Due to the long delay of some laboratories some results are no longer useful for people to isolate themselves if they have the virus. Have more rapid tests (results in minutes) that are accurate and reliable and can be taken at home or in schools or work is needed and would help a lot to really reduce the risk of contagion as we try to return to normality in society, "says Dr. Lobelo.
What are rapid tests?
There are also two types: to detect antigen or antibodies.
"The basis of the (rapid) test is immunochromatography, which is like a pregnancy test, the one where you put a drop of the sample in a container and some bands appear that show whether it is positive or negative," says Dr. Gutiérrez .
For her, rapid tests are essential because the PCR test is complicated and time-consuming.
Rapid antigen tests "have the same interpretation as PCR, they serve the same purpose but are not as sensitive. Antibody tests are used for screening, and help to interpret false positives or false negatives and are good to see that one it already gave him, "he adds.
Homemade covid-19 tests
How to test yourself for covid-19?
0:32
Coronavirus self-tests, also known as home or over-the-counter tests, detect current coronavirus infections, not antibodies to the virus, and can be easily and quickly performed at home or elsewhere, regardless of your vaccination status, say the CDC.
Most self-tests are rapid antigen tests, which may be less sensitive than PCR tests performed in clinics or laboratories.
Some home tests are PCR, but antigen versions are much more common and accessible.
With information from Carolina Melo of CNN en Español, Eric Levenson, Kristen Rogers and Arman Azad of CNN.
Pandemic