What is the NATO collective defense principle?
2:03
(CNN) --
NATO, the North Atlantic Treaty Organization, to give it its full name, is a non-aggressive European and North American defense alliance created to promote peace and stability and safeguard the security of its members.
The organization, which is based in Brussels, Belgium, was created as the Cold War intensified.
Its objective was to protect the countries of Western Europe from the threat posed by the Soviet Union and to counteract the spread of communism after World War II.
In April 1949, its 12 founders—the United States, Canada, the United Kingdom, France, and eight other European nations—signed the North Atlantic Treaty, pledging to protect each other by political and military means.
Why did Russia attack and invade Ukraine?
What are the reasons and the origin of the conflict?
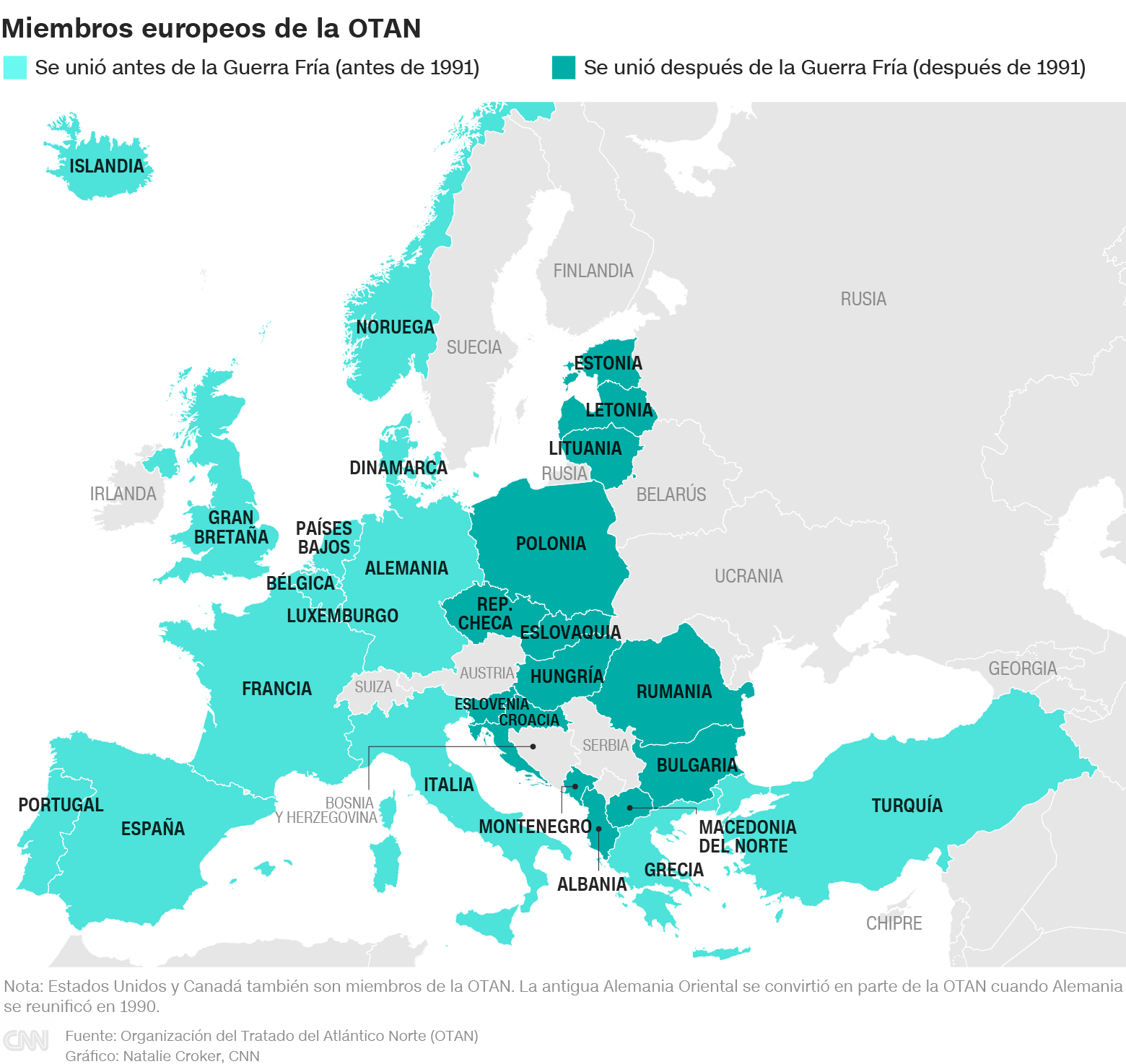
Since then, the alliance has grown: today it has 30 members.
In alphabetical order, they are: Albania, Germany, Belgium, Bulgaria, Canada, Croatia, Denmark, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, United States, Estonia, France, Greece, Hungary, Iceland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, North Macedonia , Montenegro, Norway, the Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, the United Kingdom, the Czech Republic, Romania and Turkey.
Since the end of the Cold War, more than a dozen countries from the former Eastern bloc, including three former Soviet republics, have joined the alliance.
Russia continues to see NATO as a threat despite the collapse of the Soviet Union.
Amid recent tensions with the West, Russia has asked for firm guarantees that the alliance will not expand further, something NATO members have resisted.
advertising
However, since this May, more tension has built up between NATO and Russia due to the declaration of support for NATO by the President of Finland, Sauli Niinisto, and the Prime Minister, Sanna Marin, after the Finnish government recently submitted to the country's parliament a report on national security outlining the path to joining the alliance as one of Finland's options, amid Russia's war in Ukraine.
Once Parliament has approved the idea in principle and other internal legislative hurdles have been overcome, NATO is expected to invite Finland to negotiate its accession.
Sweden, Finland's neighbor to the west, is also expected to soon announce its intention to join the alliance through a similar process.
For its part, Russia warned both countries against joining NATO, saying there would be consequences.
Latest news on Russia's war in Ukraine: the Kremlin warns of Finland's possible entry into NATO
What does the principle of collective defense mean?
Despite the great geopolitical changes that have occurred since the founding of NATO, its objective remains the same.
The key principle on which the alliance is based is that of collective defense: "An armed attack against one or more of them in Europe or North America will be considered an attack against all of them."
The principle of collective defense is included in article 5 of the North Atlantic Treaty.
It ensures that the resources of the entire alliance can be used to protect any member nation.
This is crucial for many of the smaller countries, which would be helpless without their allies.
Iceland, for example, does not have a standing army.
Since the United States is the largest and most powerful member of NATO, any state in the alliance is effectively under the protection of the United States.
In fact, the first and only time Article 5 was invoked was after the September 11, 2001, attacks on the United States;
as a consequence, NATO allies joined the invasion of Afghanistan.
However, NATO has also acted on other occasions.
It launched collective defense measures in 1991 when it deployed Patriot missiles during the Gulf War, in 2003 in the midst of the Iraq crisis, and in 2012 in response to the situation in Syria, also with Patriot missiles.
All three were based on requests from Turkey.
Finland, closer to joining NATO 1:02
Do you have your own army?
No. NATO depends on the contribution of forces from its member countries, which means that it is essentially only as strong as the individual forces of each nation.
It is in the interest of the entire coalition to ensure that each country dedicates sufficient resources to its defense.
This has been one of the main sticking points in the alliance, with the US and UK often criticizing other member states for not doing their fair share.
US military spending has always dwarfed the budgets of other allies since the founding of NATO in 1949. But the difference became much larger when the US increased its spending after the 9/11 attacks.
According to NATO guidelines, each country should spend 2% of its GDP on defense, but most countries are falling short of that goal.
Former US President Donald Trump was particularly eloquent on this issue, demanding European countries do more and, at one point, even suggesting that they "give back" the US its past deficits.
Trump: NATO Members Increased Contributions Because of My Comments
According to the most recent NATO estimates, seven member states, Greece, the United States, Croatia, the United Kingdom, Estonia, Latvia, Poland, Lithuania, Romania and France, would reach the 2% target in 2021.
Still, it's a significant improvement.
In 2014, only the US, UK and Greece spent more than 2%.
At that time, all member countries that were below the threshold pledged to increase military spending to reach the goal within a decade.
Most are keeping their promise.
How has the mission of the organization changed over time?
After the fall of the Soviet Union, NATO evolved and expanded.
Since then its members have served as peacekeepers in Bosnia, have fought against human trafficking and have been deployed to intercept refugees in the Mediterranean.
The Alliance is also responding to new ways in which conflicts can develop, for example by creating a cyber defense center in Estonia.
CNN's Frederik Pleitgen and Nadine Schmidt contributed to this report.
NATO