These are numbers that send shivers down your spine.
Vice President of Ruijin Hospital, one of Shanghai's leading hospitals in China, Chen Erzhen estimated that "
the
Covid-19 outbreak
may have affected 70% of [Shanghai's] population
", since the lifting of restrictions linked to the zero Covid policy on December 7.
This would represent approximately 18 million people.
"
It's stratospheric
"
,
launches Bruno Lina, virologist at the civil hospices of Lyon and member of the committee for monitoring and anticipating health risks (Covars).
Reported per day, this figure exceeds 600,000 daily infections.
“
It is not negligible, but it is not alarming in a population with very little immunity
”
,
adds Philippe Amouyel, epidemiologist and professor of public health at the Lille University Hospital.
” READ ALSO –
Covid-19: what if the “worst variant” was in fact in the United States?
Where is the epidemic in China?
Le Figaro
takes stock of the information available, four days before the reopening of China's borders.
How many people are infected?
Difficult to have precise estimates.
Already because China stopped massively testing its population when the zero covid measures were lifted.
“
The R0
[the number of cases generated by a single person, editor’s note]
could be between 10 and 12
, estimates Bruno Lina.
This is why the virus is circulating like
wildfire
.
“
The rate of transmissibility in China is very high
”
,
for its part confirmed the World Health Organization (WHO) during a press briefing on Wednesday.
“
This can be explained by the sudden end of the restrictive measures in a country with very little immunity, whether by a previous infection or by vaccines
”
,
adds Philippe Amouyel.
” READ ALSO –
Marie Holzman: “Covid will be China’s Chernobyl”
A few estimates, like those made for the city of Shanghai, still allow us to get an idea of the magnitude of the wave.
This is particularly the case of the province of Zhejiang (East), bordering Shanghai.
It estimated last week that a million new cases appeared every day.
The city of Qingdao (East) has reported 500,000 new daily infections, that of Dongguan (South) mentions 300,000.
In the island-province of Hainan (South), the authorities estimated on Friday December 30 the contagion rate of the inhabitants at more than 50%.
The cities of Quzhou and Zhoushan (East) have calculated that at least 30% of their population has caught Covid-19.
Data, which would have leaked from a meeting of health authorities, recently evoked 250 million contaminations over the first 20 days of December, in a country which has 1.4 billion inhabitants.
Are hospitals overwhelmed?
According to some available images, yes.
“It was also predictable
, assures Bruno Lina
.
Omicron is certainly less virulent than the previous variants take people to the
hospital
.
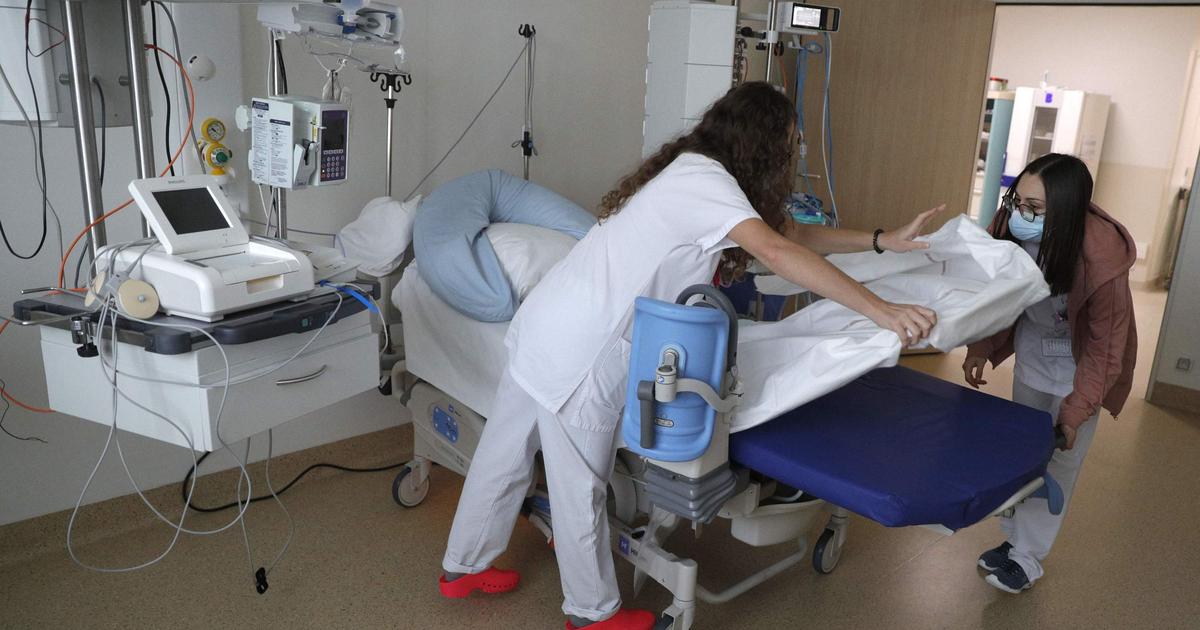
Certain scenes reported by press agencies such as AFP do indeed report hospitals on the brink of collapse.
A patient is treated on a bed in a corridor of the emergency department of a hospital in Beijing, January 3, 2023. JADE GAO / AFP
Nevertheless, it remains difficult to be precise on this question, again due to the lack of more concrete information, in particular on the number of people hospitalized.
“We believe that the current figures published by China under-represent the real impact of the disease in terms of hospital admissions, admissions to intensive care and especially in terms of deaths”
, thus advanced this Wednesday Michael Ryan , WHO official responsible for the management of health emergencies.
According to the experts interviewed, “
the Chinese hospital system is not as good as the one we have in France
”
.
A French system which had had the greatest difficulty in resisting certain epidemic waves.
Patients lie on beds and stretchers in a corridor of the emergency department of a hospital in Shanghai, January 4, 2023. STAFF / REUTERS
This Wednesday, China reported only 15 deaths linked to Covid-19, due to a change in methodology in its count since December 7.
Since December 21, only people who died directly from respiratory failure linked to Covid-19 are now counted in the statistics.
On December 15, the professor of epidemiology and public health at the University of Versailles-Saint-Quentin Mahmoud Zureik indicated to
Figaro
that certain models reported a potential number of deaths of up to one or even two million. , over the next three to six months.
” READ ALSO –
China has not been able to get out of “
zero Covid
” and is exposed to more than 1 million deaths
In particular, a lack of immunity in the Chinese population.
In particular a hybrid immunity, that is to say conferred by an infection with the virus and by the vaccines, almost non-existent.
“
The vaccines used by China
[essentially the Chinese Sinovac and Sinopharm, NDRL]
are less effective than European vaccines against infections
,
”
explains infectious disease specialist Anne-Claude Crémieux.
According to her, these European messenger RNA vaccines are themselves ineffective against Omicron infections.
“
Especially since their vaccines essentially date from 2021 and only target the original strain of the virus
[unlike the bivalent vaccines now used in Europe, editor’s note], adds virologist Bruno Lina.
They are effective only from three
doses
.
” READ ALSO –
Covid: China stumbles on messenger RNA vaccines
Vaccination rates in China are also low.
According to WHO data reported on Tuesday by the
Financial Times
, only 40% of people over 80 have received a booster dose in China.
Figures that roughly match official data reported by
Reuters
on December 21.
What variants are circulating in China?
The information so far is reassuring.
In a press release published on Wednesday, the WHO reports a “
predominance of Omicron BA.5.2 and BF.7 lines [which] would represent 97.5% of all infections
” in the country since December 1.
These are two sub-variants of Omicron which are already circulating in Europe and France.
"
A few other known Omicron sublines have also been detected, but in low percentages
," continues the WHO in its statement.
Clearly, no new variant was detected.
Nevertheless, the WHO again called on China to share more information on Covid-19 strains “
to assess mutations and detect possible new variants circulating in China
”
.
” READ ALSO –
Outbreak of Covid-19 in China: the threat of emergence of new variants
These data, transmitted to the WHO by the Chinese center for disease control and prevention, must however be taken with great caution, as they are most certainly incomplete.
They are based only on 2000 sequencings.
“
It is precisely this opacity on the real circulation of variants that is worrying
,
”
says Anne-Claude Crémieux.
What is the response from other countries?
On Wednesday January 4, the European Union (EU) “
strongly encouraged
” its member states to impose a negative test within 48 hours of travelers from China.
During a meeting of experts, the Europeans also agreed on other recommendations which it will then be up to each Member State to apply: wearing a mask is compulsory, random tests on arrival or control waste water from airports and aircraft from China.
The day before, the "
overwhelming majority
" of EU countries had already said they were in favor of such a test.
Sweden, the new president of this Council of the EU, notably assured as of this Saturday that it wanted a common response.
Last Thursday, the 27 had already met in Brussels without however agreeing on anything.
” READ ALSO –
The new explosion of Covid in China worries the world, but not Europe
For its part, France announced on Friday December 30 the imposition of restrictive measures for people from China, in particular a negative PCR test of less than 48 hours on boarding.
These will take effect this Thursday, January 5.
This Wednesday, government spokesman Olivier Véran reaffirmed that the resumption of the Covid-19 epidemic in China was
"the source of legitimate concern for Europe"
, after Beijing denounced the imposition of this test and threatened with "
countermeasures
".
So far, some 15 countries have imposed restrictions on travelers from China.
In Europe, Italy was the first to act, taking the lead on a possible joint response from Brussels.
Preceded by the United States in particular.