Blood pressure in the arteries (which carry oxygenated blood from the heart to the organs) fluctuates constantly throughout the day within a range considered normal.
But too great a voltage drop is not insignificant.
This "hypotension" is likely to induce unpleasant symptoms, or even loss of consciousness.
What are the signs of hypotension?
Is it still serious?
How to raise your blood pressure?
Le Figaro
takes stock with Gérard Helft, cardiologist at the Pitié-Salpêtrière Hospital (AP-HP) and professor at Sorbonne University.
What is pressure or blood pressure?
“
Blood pressure, also called blood pressure, is the force exerted by blood on
the
walls of blood vessels as it circulates through the body
,” explains Gérard Helft.
.
In practice, doctors distinguish between two pressures:
systolic
pressure
: the maximum pressure exerted on the blood vessels, the arteries, when the heart contracts and ejects oxygenated blood to the other organs.
diastolic
pressure
: the minimum pressure exerted on the arteries between two contractions, that is to say when the heart "relaxes" and fills with deoxygenated blood from other organs.
During an examination, the doctor takes each of the two values which are stated one after the other and expressed in millimeters of mercury (mmHg).
The pressure is considered normal when it is between 90/60 mmHg (ie a systolic pressure of 90 mmHg and a diastolic pressure of 60 mmHg) and 120/80 mmHg.
In everyday language, however, blood pressure is expressed more in centimeters of mercury (cmHg).
We will then say that normal blood pressure is between 9/6 (cmHg) and 12/8 (cmHg).
What is hypotension?
"
Hypotension corresponds to a decrease in blood pressure of more than 20 mmHg, or 2 cmHg, when going from a lying or sitting position to a standing position
", explains Gérard Helft.
We will then speak of
orthostatic hypotension or postural hypotension
.
When orthostatic hypotension occurs right after a meal, it is called
postprandial hypotension.
"
This is explained by the fact that after having fed the digestive system will require a large quantity of blood to the detriment of the cerebral vascularization
", explains the cardiologist.
In case of hypotension, there is a risk that all parts of the body are not sufficiently "irrigated".
Some organs may lack oxygen or nutrients, and waste products may not be properly eliminated.
” READ ALSO –
Why blood pressure is the big indicator of your state of health
What are the symptoms ?
Whether it is orthostatic or postprandial hypotension, the symptoms are similar: dizziness, dizziness, a feeling of having a veil over the eyes, nausea and generalized weakness.
"
In the most serious cases, hypotension causes loss of consciousness (
syncope
) as well as a loss of postural tone, which increases the risk of potentially serious falls, such as those resulting in a
fracture of the neck of the femur", indicates the Pr Helft, especially in the elderly.
In the latter, hypotension is also likely to lead to a state of shock.
Too sudden a drop in voltage can indeed damage the normal functioning of essential organs, such as the brain and the kidneys.
If the drop in blood pressure is not accompanied by any symptoms, then "
there is nothing to worry about
", specifies the doctor.
Too low blood pressure is less harmful to the cardiovascular system than hypertension.
In this second case, the arteries tend to tighten, forcing the heart to work harder to pump blood, which increases the risk of myocardial infarction, for example.
What are the main causes of hypotension?
While everyone can experience a drop in blood pressure from time to time by getting up too quickly, the problem is sometimes more systematic.
The main risk factors are:
Age:
older people are more likely to experience drops in blood pressure when getting up because aging naturally leads to a stiffening of the blood vessels.
Since the walls of the latter are less elastic, blood pressure cannot adjust as quickly as in young people.
“
That's why hypotension affects older people more often.
It is generally estimated that this concerns 10 to 15% of the population over the age of 65
, ”underlines Professor Helft.
Pregnancy:
In pregnant women, blood pressure tends to decrease naturally.
On the one hand because the entire circulatory system is directed towards the fetus, but also because hormonal changes (in particular the increase in progesterone levels) tend to dilate the blood vessels, which mechanically lowers the pressure.
But hypotension can also have other causes, whether they are:
Acute
: Severe dehydration, vomiting, or heavy bleeding can cause an unusual drop in blood pressure as the body struggles to compensate for losing fluid too quickly.
Neurological
: certain neurological diseases, such as Parkinson's disease or multiple sclerosis, promote hypotension by altering the detection of blood pressure by the autonomic nervous system (which acts unconsciously).
Drugs:
certain molecules sometimes cause dilation of the arterioles, the small branches in the arteries.
This is typically the case with diuretics and some antidepressants.
Nevertheless, dilation of the arterioles can also occur in the event of severe infections, allergic reactions or in people suffering from endocrine disorders (insufficient or excessive release of hormones in the body).
Physical:
if a subject is ill and remains lying down for a long time, the sudden transition to a standing position can cause orthostatic hypotension.
This is called deconditioning.
W
hat tests to diagnose a voltage drop?
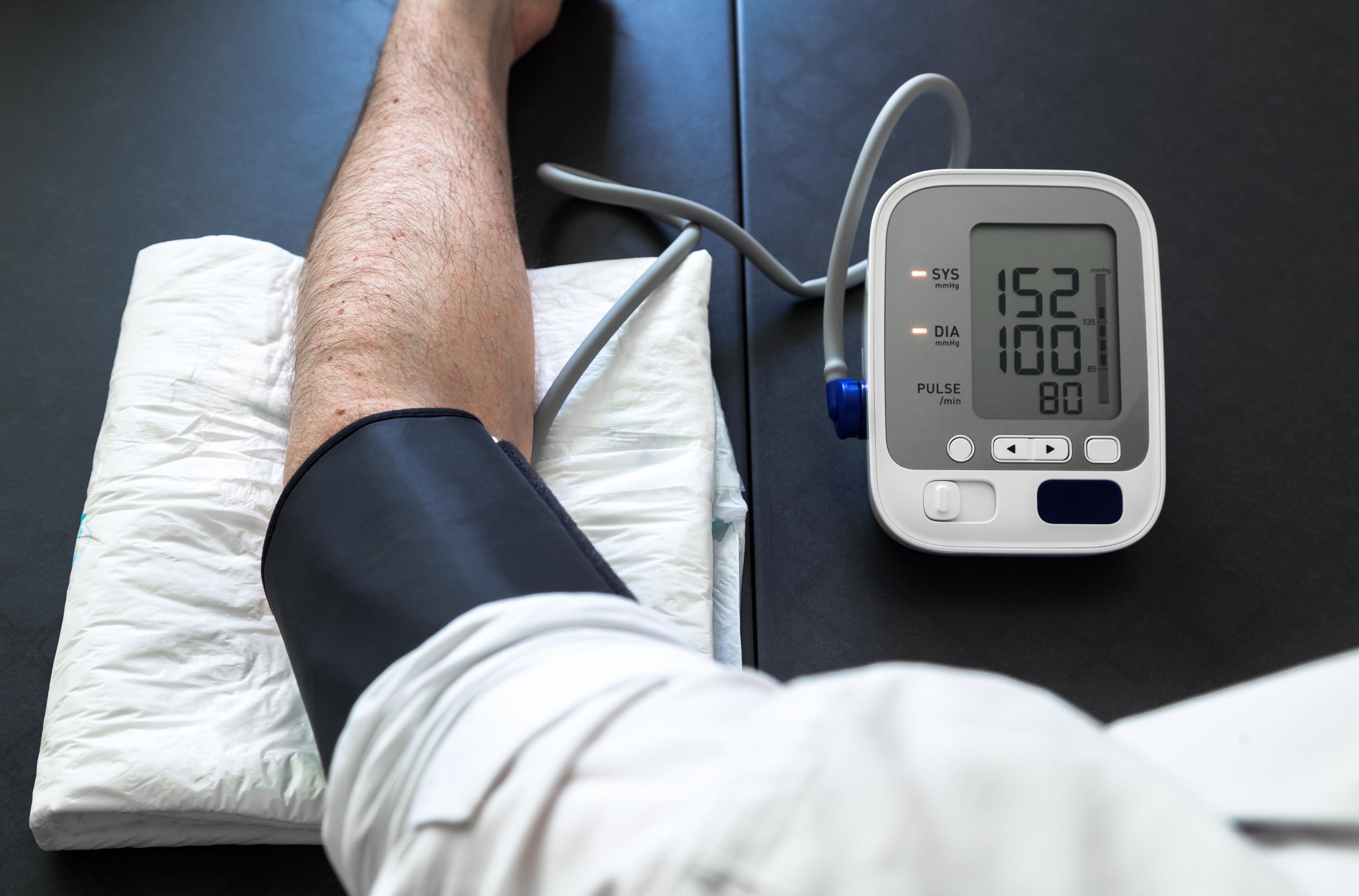
The doctor measures the patient's blood pressure twice using a blood pressure monitor, first at rest in a lying or sitting position and then in a standing position.
"
If the blood pressure drops by more than 20mmHg within 3 minutes after getting up, then it is orthostatic hypotension
", explains Gérard Helft.
For subjects familiar with blood pressure problems or suffering from cardiovascular diseases, it is particularly recommended to bring a blood pressure monitor at home in order to carry out a pre-diagnosis yourself when you think you have characteristic symptoms.
Such devices can be bought in pharmacies and are easy to use.
However, they do not in any way replace a medical visit because only a general practitioner can determine the causes and prescribe an appropriate treatment.
” READ ALSO –
Measuring your blood pressure: vital to prevent risks
How to raise your blood pressure?
"
If we have succeeded in identifying the cause, we can easily treat the patient by acting at the root of the problem
", explains Gérard Helft.
If the drop in blood pressure coincides with taking medication known to disrupt blood flow, the doctor will recommend to stop replacing it with another or to stop it if not essential.
Depending on the patient, a problem of hypotension can be treated using simple lifestyle and dietary measures.
"
We can recommend increasing the proportion of salt in your diet to 6 to 10g per day
," says the cardiologist.
Normally, salt is not recommended because it promotes hypertension.
However, it can help to raise a pressure that is too low because sodium chloride works by retaining water in the arteries.
However, it is important to seek the advice of a doctor before taking the initiative to increase salt consumption because "
an individual with hypotension can also suffer from hypertension or even heart disease, which risks to worsen his state of health
", warns the cardiologist.
Other hygienic measures will consist of wearing compression stockings to prevent the blood from stagnating in the legs.
It is also advisable to stay well hydrated, to avoid alcoholic beverages, not to expose yourself to excessive heat or to eat too large meals.
Certain high-sodium drinks, coffee and tea can also be beneficial for stimulating circulation, but may dehydrate the body in the long run.
"
If these measures are insufficient, it will be necessary to go through drug treatment
", underlines the cardiologist.
The drug most often prescribed is fludrocortisone (Florinef) but there are others.
In all cases, medical advice is necessary to avoid the risk of complications.




/cloudfront-eu-central-1.images.arcpublishing.com/prisa/XOCFAYPRIQDLM7PDZZL34XDWTI.jpg)




/cloudfront-eu-central-1.images.arcpublishing.com/prisa/2C5HI6YHNFHDLJSBNWHOIAS2AE.jpeg)



