Researchers produce "xenobots" - new life forms that are made up of stem cells and act like robots • They can heal themselves, walk, swim and work collaboratively
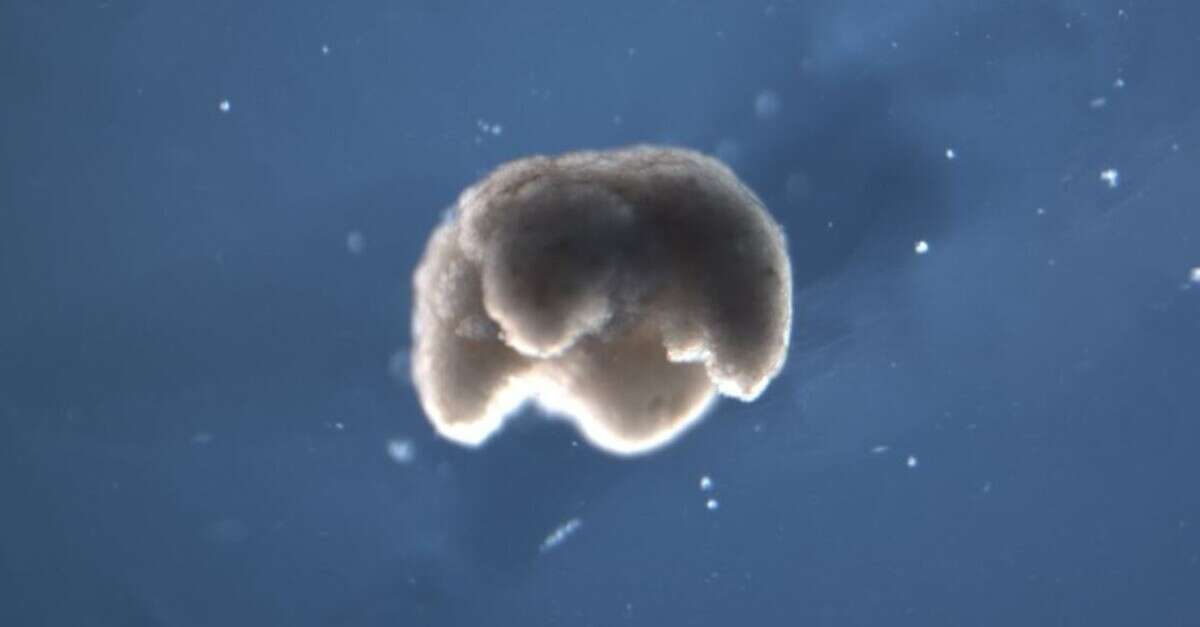
Between frog and robot - scientists have created a new way of life. Researchers at the University of Vermont and Tufts University assembled "xenobots," stem cells of frog embryos. According to a report on the Anajet website, the xenobots are small millimeter-wide chunks that act like living robots and heal themselves. They can walk, swim and work collaboratively. They can also be used to reprogram tumors within the human body, transfer drugs, or scrape plaque outside the arteries.
From the University of Vermont YouTube channel
"These are new living machines," said Joshua Bongard, a computer scientist and robotics specialist at the University of Vermont who is among the leaders of the new study. "They don't act like traditional bots, and no known animal species. It's a new kind of object: a living, programmed organism."
To determine the best design for the new way of life, researchers at the University of Vermont ran an evolutionary algorithm using a supercomputer. Tufts University researchers then assembled and examined the design using the skin cells and heart cells of African frogs of the Xenopus laevis strain, hence the name of the robotic stem cells.
The team of scientists created a body shape that was never seen in nature. The cells work together and allow the robots to move on their own in aqueous environments. They even cooperated spontaneously to move around circles and push spheres to a central location.
According to the researchers, unlike robots made of steel or plastic, the advantage of the xenobots is that they will fall apart after use. When cut, they are able to regenerate and sew themselves together, an action that single robots are capable of doing. In addition, they can be used for medical purposes, radioactive waste cleaning or microplastics.
Researchers say the job is designed to achieve more than just creating squid-like robots. "The goal is to understand the software of life," said Guardian newspaper Michael Levine, director of the Allen Discovery Center at Tufts University. "If you think of birth defects, cancers or age-related illnesses - all of these things could have been solved if we were able to produce biological structures to have final control over growth and shape."
The xenobots are pre-loaded with their own food source, which should end after about a week, unless they are in a nutrient-rich environment. However, at least at this point, these small chunks cannot reproduce or develop.
"There are interesting ethical questions about the moral state of the xenobots," said Thomas Douglas, senior research associate at the Center for Practical Ethics at Oxford Oyero. "At what point are they already considered to be protected interests? I think they would only have moral significance if they included neural tissues that allow some mental life, like the ability to experience pain.
"But there are more liberal people regarding the moral status of these creatures. They think that all living things have attributes that need to be given some moral consideration. For these people, difficult questions may arise about whether the xenobots should be classified as living creatures or machines."