Enlarge image
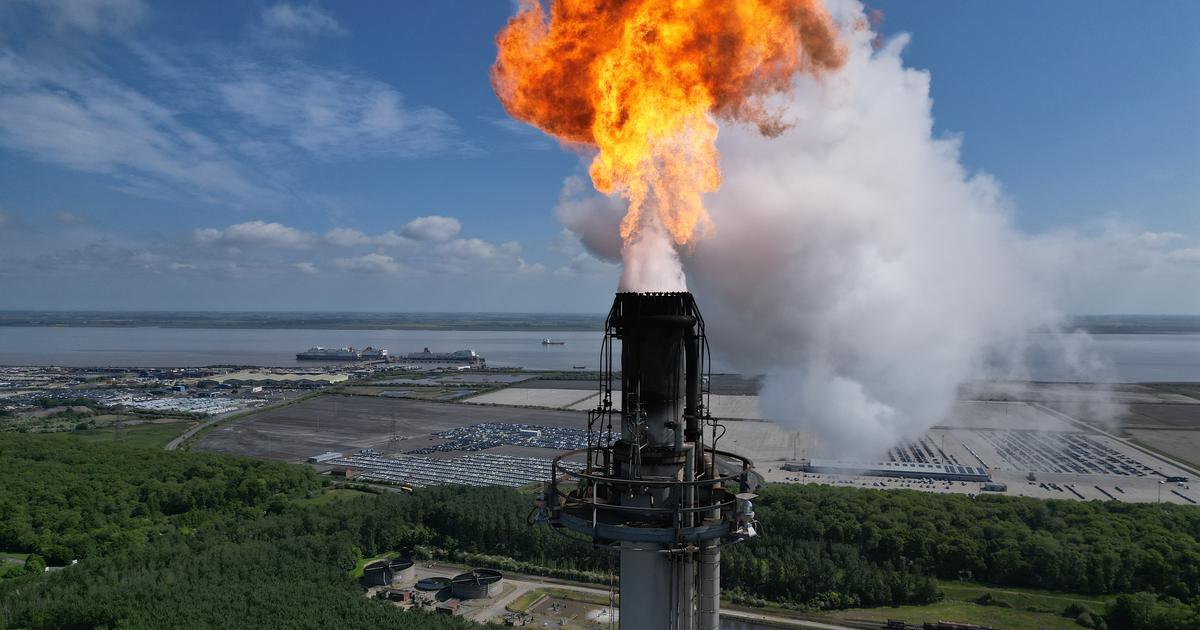
Coal mine in Russia: Also a question of safety
Photo: Andrey Rudakov/Bloomberg/Getty Images
A private satellite company tracking sources of methane emissions around the world has discovered one of the largest man-made sources of this climate-damaging greenhouse gas ever observed.
As announced by the Montreal-based company GHGSat, one of their satellites has struck gold in Russia.
»Hugo« discovered 13 methane plumes in the Raspadskaya mine in Siberia on January 14th.
According to the company's calculations, about 90 tons of methane were released into the atmosphere within one hour during this incident in the city of Mezhdurechensk.
It may have been the largest known methane leak to date.
Manfredi Caltagirone, director of the International Observatory on Methane Emissions at the United Nations Environment Programme, said he was not aware of any major release of methane from a coal mine.
"It was a really dramatic release," said Brody Wight, GHGSat's Energy, Landfill and Mining Specialist.
According to the company, the amounts of methane discovered at Mezhdurechensk may have been released intentionally to ensure safety at the mine.
The gas can ignite underground - with fatal consequences for the miners.
Two methane explosions and a fire killed 91 people at this mine in 2010, one of the worst disasters of its kind in the post-Soviet era.
Release was not an isolated case
However, it is possible to prevent the uncontrolled release of methane by certain methods.
The captured gas could then be used as fuel - this reduces the climate-damaging effect.
According to GHGSat, the release of methane in the mine was not an isolated case.
Further satellite measurements in the coming weeks revealed additional gas plumes.
But none reached the magnitude of January 14.
The company said it had informed the Raspadskaya colliery, Russia's largest hard coal mine, of the findings, but received no response.
The Associated Press's request for comment also went unanswered.
In recent years, several private and government satellites have been launched to detect methane leaks and raise awareness of the gas's risks.
One of the most notorious methane leaks in the United States erupted at a natural gas storage facility in California in 2015.
Residents of the San Fernando Valley also fell ill - 8,000 houses had to be evacuated.
Methane (chemically CH4) is an odorless and colorless gas.
It enters the atmosphere through natural sources such as swamps and moors, but also through emissions from industry, the use of fossil fuels or agriculture, especially animal husbandry.
Methane emissions have increased globally in recent years.
According to data from the US agency NOAA (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration), the concentration rose in 2021 to the highest level ever measured.
Methane is considered to be more harmful to the climate than carbon dioxide.
Over a period of 100 years, methane has a 28 times greater climate impact than CO₂, and over 20 years the impact is 86 times greater.
If methane emissions were reduced by 45 percent, the global average temperature could be reduced by 0.3 degrees Celsius from 2040, according to the United Nations Environment Program's methane report.
joe/AP