A treasure trove of
dormant stem cells
, precious for the
repair of lesions of the central nervous system
, has been
discovered in mice
by researchers at the Francis Crick Institute in London: if its existence is also confirmed in humans, it could pave the way for new strategies. of regenerative medicine to repair damage to the brain and spinal cord, as indicated by the study published in the journal Developmental Cell.
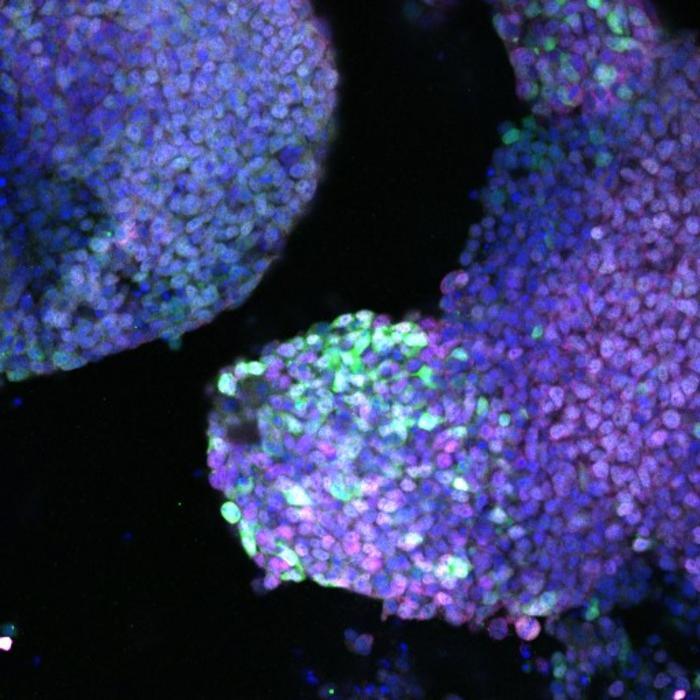
The dormant stem cells of the central nervous system are part of the so-called
ependymal cells
that
line the cavities of the cerebral ventricles
and the
canal of the spinal cord
where the
cerebrospinal fluid
is contained .
Researchers
discovered them by accident
while trying to label some immune cells in the brain.
Thanks to the collaboration with the Lisbon Institute of Molecular Medicine, they observed that in healthy mice these ependymal cells remain dormant: their task is to
move the cerebrospinal fluid
by waving the cilia present on their apical surface.
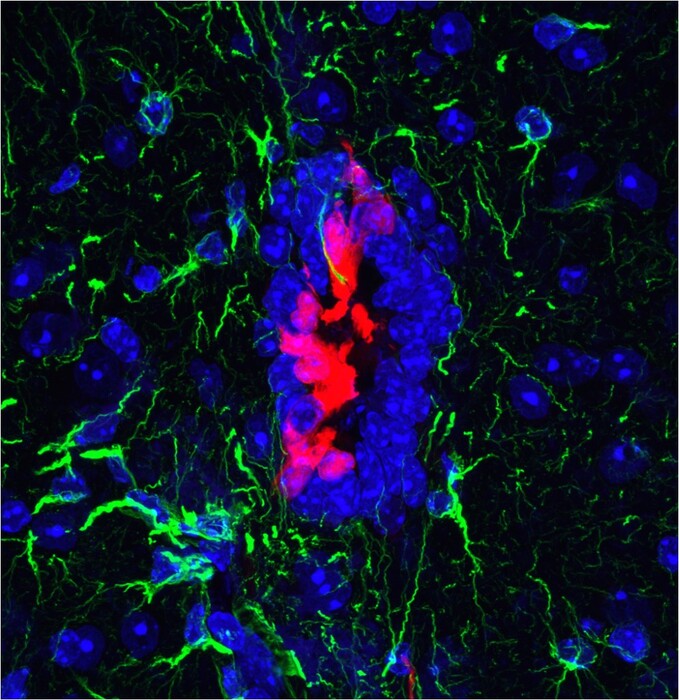
In the case of a spinal injury
, however, these cells
awaken
and begin to divide,
migrating
to the lesion where they differentiate into astrocytes, one of the main cell types of the nervous system.
These ependymal cells show all the
typical characteristics of stem cells
: they divide continuously for a long time and are able to differentiate into all three cell types of the central nervous system (ie neurons, astrocytes and oligodentrocytes).
"
We still don't know if these cells also exist in humans
, but if there were - explains Bruno Frederico of the Francis Crick Institute - it would be interesting to understand if they too differentiate into astrocytes instead of neurons in response to damage.
This may explain why the mammalian central nervous system does not have a great ability to repair itself.
If we can find a way to overcome the obstacles that prevent differentiation into neurons and oligodentrocytes, we could have new therapies to treat spinal injuries. "

/cloudfront-eu-central-1.images.arcpublishing.com/prisa/QZBKEHFL6RHI5FSPQNNBZGIIUA.jpg)
/cloudfront-eu-central-1.images.arcpublishing.com/prisa/4BBEMCOSQFE7LNGAOSXIRE24NE.jpg)