The European Space Agency (ESA) on Thursday selected a probe, EnVision, to explore Venus in the early 2030s, in order to understand how the planet, our closest neighbor, has become an uninhabitable toxic hell.
This announcement comes a week after NASA's announcement of two new missions to Venus, between 2028 and 2030.
Read also: Space: soon a European NASA?
Have "a global view of the planet"
The EnVision probe, which competed with another mission called Theseus, was ultimately selected by ESA's science program committee for its "
breakthrough
"
technology
, the agency (22 member states) said in a statement. The orbiter will embark a series of European instruments making it possible to offer "
a global view of the planet, from its inner core to its upper atmosphere, in order to determine how and why Venus and Earth evolved so differently
".
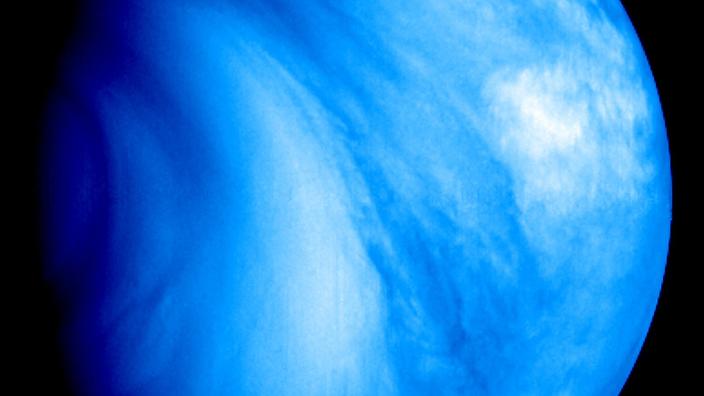
Venus may have roughly the same size and composition as the Earth, it has experienced dramatic climate change, evolving "
in a toxic atmosphere and is enveloped in thick clouds rich in sulfuric acid
", details the ESA.
To read also: Manned flights: "Europe must position itself" for the Moon or Mars
Take off between 2031 and 2033
The closest EnVision launch opportunity is 2031, and other options are possible in 2032 and 2033. After takeoff, EnVision will take approximately 15 months to reach its destination, and an additional 16 months to set its orbit, inclusive. between 220 and 540 km above Venus.
The on-board spectrometers will monitor the gases in the atmosphere and analyze the composition of the surface, "
looking for any changes linked to signs of active volcanism
". A radar provided by NASA will send images and maps of the surface. An instrument will also make it possible to probe the internal structure of the planet and its field of gravity. The previous ESA Venus Express mission (2005-2014), was mainly focused on atmospheric research.




/cloudfront-eu-central-1.images.arcpublishing.com/prisa/CCC42XRXIFAABOWMHO4KH3D7DU.jpg)


