How the immune system ages 1:21
(CNN) –– Aging is an inevitable process, but scientists from the University of California at San Diego (UCSD) may be one step closer to delaying it.
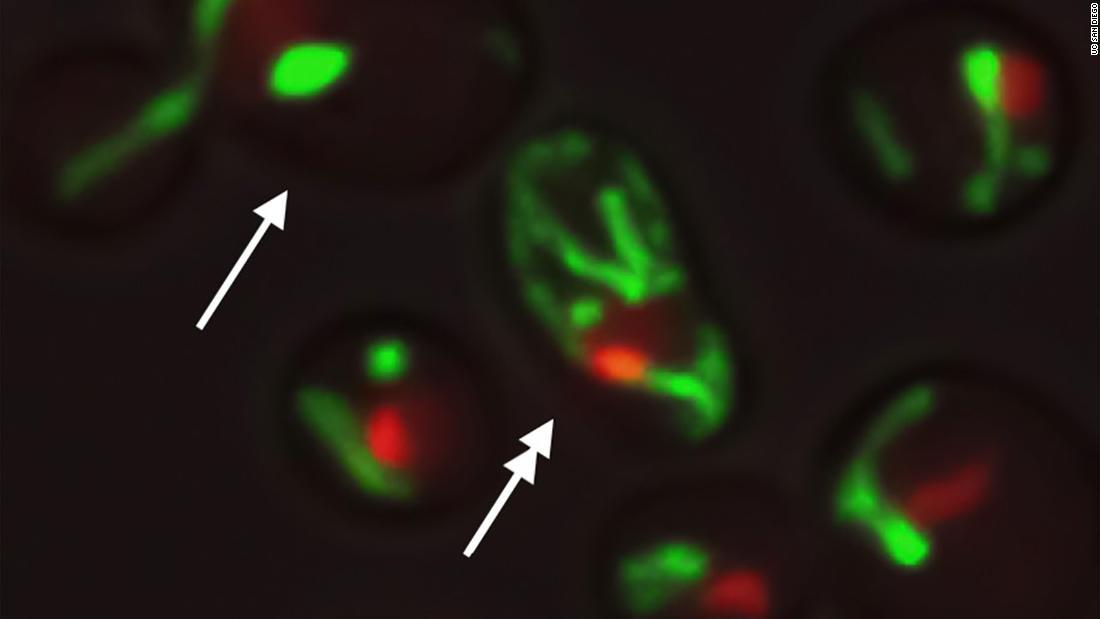
Yeast cells with the same DNA and in the same environment revealed different structures of the mitochondria (green in color) and the nucleolus (red in color), which may be the basis of the causes for different aging pathways.
A team of scientists studied aging in yeast - chosen because its cells are easy to manipulate - to try to understand if different cells age at the same rate and for the same reason.
What they found was intriguing. Even cells with the same genetic material and within the same environment aged in "surprisingly different ways," according to the researchers, who published their findings in the journal Science.
About half of the yeast cells aged due to a gradual decrease in the nucleolus, a round body located in the nucleus of a cell, according to what the scientists discovered using techniques that include microfluidics and computer modeling.
At what age do we start to age? 3:57However, the other half aged due to a dysfunction of the mitochondria, which produce the energy of a cell.
Scientists indicated that cells go one of two ways –– nuclear or mitochondrial–– at the beginning of life, and continue on the path of aging until they finally deteriorate and die.
The researchers conducted more tests to understand the behavior of the cells.
"To understand how cells make these decisions, we identified the molecular processes underlying each aging pathway and the connections between them, revealing a molecular circuitry that controls cell aging, analogous to the electrical circuits that control household appliances." explained Nan Hao, lead author of the study and associate professor in the molecular biology section of UCSD's division of biological sciences.
- READ: Is there a normal way to grow old? Scientists explain it decade by decade
After modeling the "aging landscape," the team of researchers discovered that they could manipulate - and optimize - the aging process with computer simulations to reprogram the master circuit and modify its DNA.
Then they were able to create a "new aging route," with a dramatically extended shelf life. Scientists believe that this could lead to the possibility of delaying human aging.
"This is an aging route that never existed, but because we understand how it is regulated, we can basically design or regulate a new aging route," Hao told CNN.
"Our study raises the possibility of rationally designing gene or chemical-based therapies to reprogram the way human cells age, with the goal of effectively delaying human aging and extending human health," Hao said in a statement.
What does it mean to grow old? 1:27The scientists said they plan to test their model on complex cells, organisms, and ultimately humans, as well as to test how combinations of therapies and drugs could lead to increased longevity.
"Aging is a fundamental biological issue. We know very little about the aging process, ”Hao told CNN. When it comes to medical relevance, he added, "aging is linked to many diseases, so if we can help delay aging or promote longevity, it will be beneficial to society."
cells Aging Research