Is it possible to bring the dinosaurs back to life?
Depends on who you ask
After we were informed that the uncle bird was about to return to our lives thanks to science we set out to see if the same technology could bring the dinosaurs back as well and what the consequences of such an act would be.
Forget everything you saw in the movies, because the reality is much scarier
Yaron Zilberstein
07/04/2022
Thursday, 07 April 2022, 23:35 Updated: 23:43
Share on Facebook
Share on WhatsApp
Share on Twitter
Share on Email
Share on general
Comments
Comments
Trailer for the movie "Jurassic Park" (Universal Movies)
Will we soon see in reality the sign - "Welcome to Jurassic Park"?
This week we were informed that the Dudu bird, which became extinct 300 years ago may return to our lives thanks to its genome sequencing and DNA reconstruction combined with genetic engineering, so if we open the gates of the extinct zoo - the first option that comes to mind is the return of dinosaurs.
But first one has to ask is it possible and then one has to ask do we even want it?
For those who watched the "Jurassic Park" film series, it is possible that the dinosaur character has already been implanted in a brain bothered by the terrifying scenes of park rangers turning into light meals, or we are imagining herds of long-necked animals marching across the country.
With such a large variety of species, the thrill of visiting such a dinosaur park cannot be denied.
But is the idea behind Jurassic Park really realistic?
Is it possible to bring the dinosaurs back to life?
We imagine herds of long-necked animals walking around the country (Photo: Giphy)
When Michael Creighton first coined the story of "Jurassic Park" in the late 1980s, one of the last things he wrote for himself is perhaps the most significant - how will the scientists in the story obtain the DNA needed to create a dinosaur theme park?
This was supposed to be the key to the whole plot and give the story a sense of scientific realism.
Eventually, Creighton was inspired by a scientific paper he read, which included an interview with the paleobiologist George Poyner Jr..
The article, published in the journal Science in 1982, addressed a fly that was found preserved in hardened wood resin.
Somehow, at the end of his life, the fly found himself immersed in a resin that had become a kind of time capsule.
It was not just a brilliant idea by a writer that led to the creation of this fictional park, but a scientific discovery from real life.
Together, the story of "Jurassic Park" and the science at its center inspired the next generation of paleontologists, opening the world's imagination to the possibility of returning dinosaurs.
According to livescience magazine, when it comes to dinosaurs humans have plenty of unanswered questions, and only hints at answers to their pre-modern dominance - what did dinosaurs really look like, and how did they survive for millions of years in diverse groups?
Because humans have never lived alongside dinosaurs, no one has complete answers to these questions.
We continue to learn more and more about dinosaurs, thanks to scientists who are discovering and researching more and more fossils - with more than 700 species of dinosaurs discovered so far around the world.
More on dinosaurs
How many rex lived on Earth?
Researchers have found a way to determine - and the number will amaze you
To the full article
Scientists all over the world are now working to reverse the extinction - the return to life of animals that disappeared from Earth long ago.
By editing the genetic code in the DNA of the closest living relatives of extinct animals, scientists can slowly engineer back and create a model of the DNA of the species.
One of the most publicized cases is that of the woolly mammoth, which became extinct about 4,000 years ago.
Mammoth DNA has been found stored in the frozen soil of Siberia, so scientists are working on a project to combine fragments of this genetic code with that of live elephants.
Although there are thousands of years separating these species - and more than 60 million years in the case of dinosaurs - if scientists can produce these extinct species, this may be the beginning of the establishment of a true Jurassic Park.
Extinct 60 million years ago - and will they return soon? (Photo: Giphy)
More on the subject
"The size of a basketball court": This is the largest dinosaur ever discovered in Australia
"The dinosaurs did not become extinct because of an asteroid - but because of the sex lakes"
Pesach without pain and with a special operation at Bee Cure Laser
Did we find dinosaur DNA?
The biggest hurdle that needs to be overcome before we can recover a dinosaur is how to obtain the main ingredient.
Without access to the DNA of dinosaurs, researchers could not clone real dinosaurs.
While new fossils are being discovered daily, while they can provide important evidence for their shape, the organic matter that made them up has long since disappeared.
Instead of bones, dinosaur fossils are composed of rock and sediment that have filled the bone.
These findings can tell us about the shape and size of the animal, the time it was alive and what unique traits it had, but they are unable to give us the crucial genetic information.
By 2020, researchers from the U.S. and China have discovered cartilage that they believe contains dinosaur DNA, according to a study published in the National Service Review. The dinosaur (Cretaceous-type hypocrosaurus) may be over 70 million years old - but it has calcified and petrified, which may have protected the inside of the cells.
A year later it was reported that a team of Chinese and American researchers announced that they had found what appeared to be DNA in the fossil of a 125-million-year-old dinosaur - although the question of how the fragile biomolecules survived the fossil remains a mystery.
Alida Beiluel, a paleontologist from the Chinese Academy of Sciences and colleagues found the biomolecules in a part of the cartilage of Caudipetrics, a peacock dinosaur that was the size of a peacock and lives in what is now northeast China - and is one of the oldest feathered dinosaur species ever discovered.
The scientists who published the study are optimistic about whether it will be possible to recover the DNA of the dinosaur from their findings.
It would be fantastic if the authors of the article were right and they would be able to identify the nucleic acid, or other biomolecule, of a dinosaur - in which case the potential would become very realistic.
A five-meter-long dinosaur tail fossil was discovered in a desert in northern Mexico, July 2013 (Photo: Reuters)
Can we really create a dinosaur?
So now it remains to ask - will it ever be possible to return a dinosaur from extinction?
This is a question that scientists all over the world are trying to find the answer to, even though the process will be completely different from how it is presented in movies.
“We think we found signs of DNA and small pieces may have remained, but not enough to create a dinosaur.
We can get collagen and some dinosaur protein, but not all the stuff we need, "said paleontologist Jack Horner.
" Even if we had the DNA, it would be ridiculous to put it in an ostrich egg.
The right thing to do would be to grow it in vitro, because we have no idea how big the embryos of all the dinosaurs are.
Some dinosaur eggs may be the size of ostrich eggs, but for example for the Tyrannosaurus rex, we think they were much longer and larger.
It's like trying to put a human embryo inside a squirrel. "
Horner is the true paleontologist who inspired the character of Alan Grant (played by Sam Neil in the movie "Jurassic Park"). And gave the name to the species of dinosaurs from
Isura
. He was also the consultant to the paleontology of the Jurassic Park films. And while he sees the cloning process as completely fictional, it did not stop him from trying to bring the dinosaurs back to life.
, "He discovered," it's called the Dino-Chicken Project, and it's mostly based on genetic engineering.
The idea is to use hereditary (atbistic) genes.
Which are in fact genes of their ancestral ancestors, i.e. animals in which their ancestors programmed certain traits.
For example, sometimes children are born with additional vertebrae that form a kind of tail, which the doctor simply picks up only when the child is born.
Horner's plan is to take advantage of these atbistic genes.
"I was hoping that some of the characteristics of a dinosaur would be atheistic in birds. All kinds of birds are related to each other, with one common ancestor - dinosaurs - so each bird can fit. Chickens are the easiest thing to get eggs from, so I built a lab, hired some geneticists and evolutionary biologists and started. "Check to see if we can find some of these potential atheistic genes," he said.
"We work mostly on the tail, because that's the hardest part," he explained, "we found that shortening the tail from the long-tailed dinosaur to the short-tailed bird is not an atbyistic gene. We try to understand how the tail really works and reverse the process that created the short tail."
So, are we any closer to creating a dinosaur today?
"Other labs have tested the face, teeth, arms and hands. I think we can do pretty much the rest of the body. We have the potential to create an animal that has a dinosaur-like head, probably with teeth inside, and we definitely have the ability to turn the wings. "To create arms and hands. We know we can do it, but right now we're just trying to fix the tail," Horner said.
More on Walla!
A dinosaur remains were found that died from the asteroid impact that led to the extinction of the species
To the full article
Live with dinosaurs
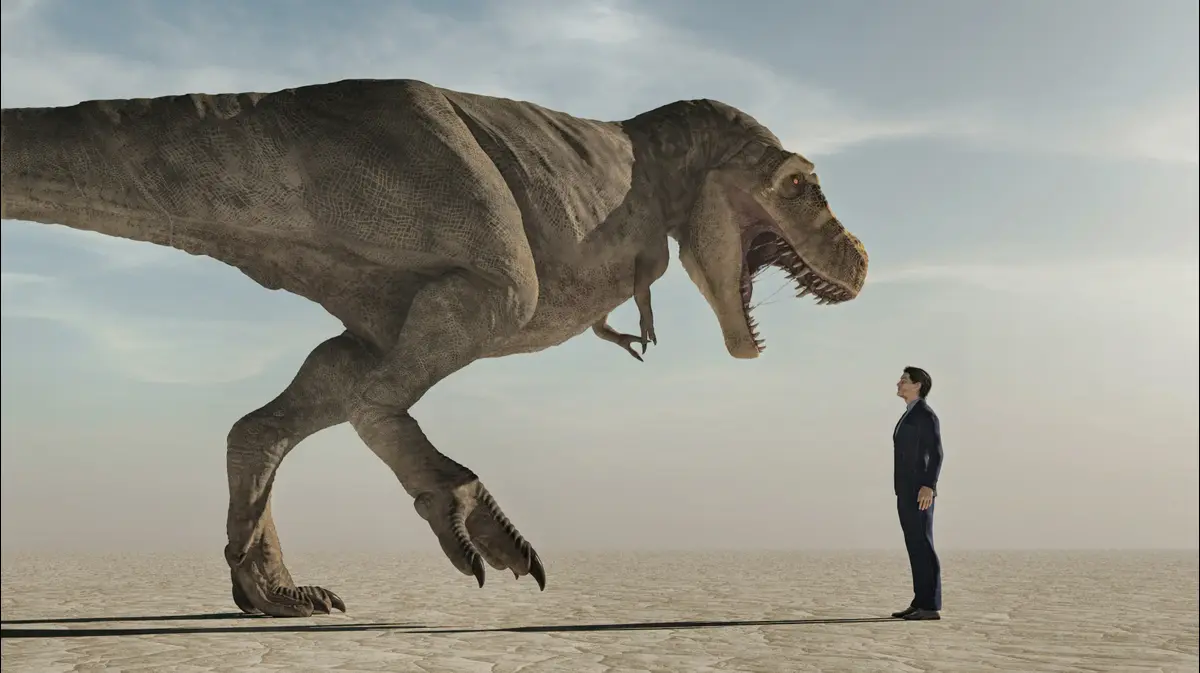
Businessman meets Tyrannosaurus Rex on the street (Photo: ShutterStock, Orla)
Let’s say humans will indeed be able to bring the dinosaurs back from extinction - how would we survive together?
If the dinosaurs were not extinct, humans would probably not have been able to evolve.
During the 150 million years that dinosaurs existed, there were mammals that lived next to them, but these were nocturnal animals that lived in burrows.
This suggests that this was the only way for mammals to survive alongside dinosaurs - to emerge mostly at night to hunt.
Because today our lives are completely separate from those of the dinosaurs, there is no way to know what will happen if the dinosaurs live on the same land as us.
By observing human behavior in the face of today's great predators, it seems unlikely that the two species would live together naturally.
Humans occupy so much space on Earth that a situation where predators like dinosaurs live out of captivity will likely result in a battle for life and death on the ground.
Horner, on the other hand, has a different view.
"People always say, 'Where do you put these dinosaurs when you make them?'
"And I always say that thousands of years ago we started with wolves, and now we have Chihuahua," he said.
Dogs are actually wolves, and we should not really contain them. I would not expect dino-chickens to be like the dinosaurs in Jurassic Park. They are going to be pets that we do not have to worry about. "Very, but the dogs and cats were also wild and today we live with them in our homes."
T Rex in Jurassic Park (Photo: Giphy, official website)
Even if we say that the issue of dinosaur restoration will be decided and we will indeed succeed in doing so - the question still remains whether we can keep them alive?
Several studies conducted on air trapped in amber show that its composition during the Cretaceous was probably 35% oxygen, compared to 21% in our air today, according to a New Scientist publication.
However, during the long time that dinosaurs lived on Earth, this number apparently changed and was significantly varied.
Thus, some species of dinosaurs will be more suited to our air than others.
Also, experts determined that when the dinosaurs roamed the earth, the global temperature was much higher than it is today, according to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.
An island in the tropics of the earth would be the best bet as a place that would provide temperatures that many dinosaurs would feel comfortable living in.
In terms of inclusion, the park will have to look completely different from how it appeared in the film.
"If you really, but seriously, want to build 'Jurassic Park' and not just the one that exists in the film, you owe walls around the dinosaurs to keep them," Horner said, adding that concrete would work much better than electric fences because "electricity can stop. The trams in the film were not a particularly good idea. "
Can we live with the dinosaurs? (Photo: Giphy)
The dinosaurs will return - in 2050?
This may sound absurd, but some experts have even set a date and contracts that humans can return the dinosaurs from extinction in some way by 2050. In fact, as early as 2016 the Adam Smith Institute's thinking teams confidently believed that humans could revive dinosaurs by the year 2050. In distractify it was reported that the institute's director Dr. Madsen Piri wrote in the report: "The dinosaurs will be re-created by a process of hybridizing backwards from flightless birds. The birds are modern-day dinosaurs, but they just no longer look like dinosaurs."
Reversal hybridization is a type of artificial manipulation for the breeding of domesticated animals in order to recreate animals with external features similar to those that existed in their extinct ancestors.
Although reverse hybridization activity can indeed "create" an animal that is similar in its external features, exists in the same ecological niche and even has several genetic characteristics similar to those of its ancestors, the original gene pool of the extinct animal cannot be restored.
In fact, backward hybridization does not recreate the extinct animal but at most an animal reminiscent in some of its external characteristics of its ancestors.
Attempts are being made these days to bring back to life in this process the wild bull, the European wild horse and the kouga (an extinct subspecies of the zebra).
The experts at the Adam Institute are convinced that the process of creating a living and breathing dinosaur will be realized thanks to DNA isolation technology.
Dr. Madsen explained, “Deep within their DNA will be information relating to the time they did so, and with the help of a combination of selective breeding and gene technology it will be possible to give them the characteristic features of dinosaurs - jaws with teeth, tail, small front limbs and more.
By isolating DNA, scientists will be able to discover "this buried information to bring out the desired properties."
The institute argued that successful development of one dinosaur embryo would eventually make it possible to produce other species in exactly the same way.
So it's true we're still a few decades away from it all, but the idea of living in the world with a real Jurassic Park is not as far-fetched as you might think, but Hendrik Poyner, a DNA research expert and director of McMaster's ancient DNA center, warns that It is dangerous to bring back ancient species of extinct animals.
"I think bringing them back because of some magical ideal is a bad idea. Scientists may think they understand the behavior of these animals, but no one has left instructions on a cave wall that explain their daily routine. Reproduction can also lead us in a dangerous way. "Just look at the dogs: we have a lot of breeds with breathing problems, dysplasia and the list goes on. About 99 percent of all species that have ever lived have become extinct - and we need to keep them in the past."
news
Not to be missed
Tags
Dinosaur
Dinosaurs
Jurassic Park
dna
extinction


/cloudfront-eu-central-1.images.arcpublishing.com/prisa/XK5OFMM65VG2ZKWHWFQNQ3A6OY.jpg)